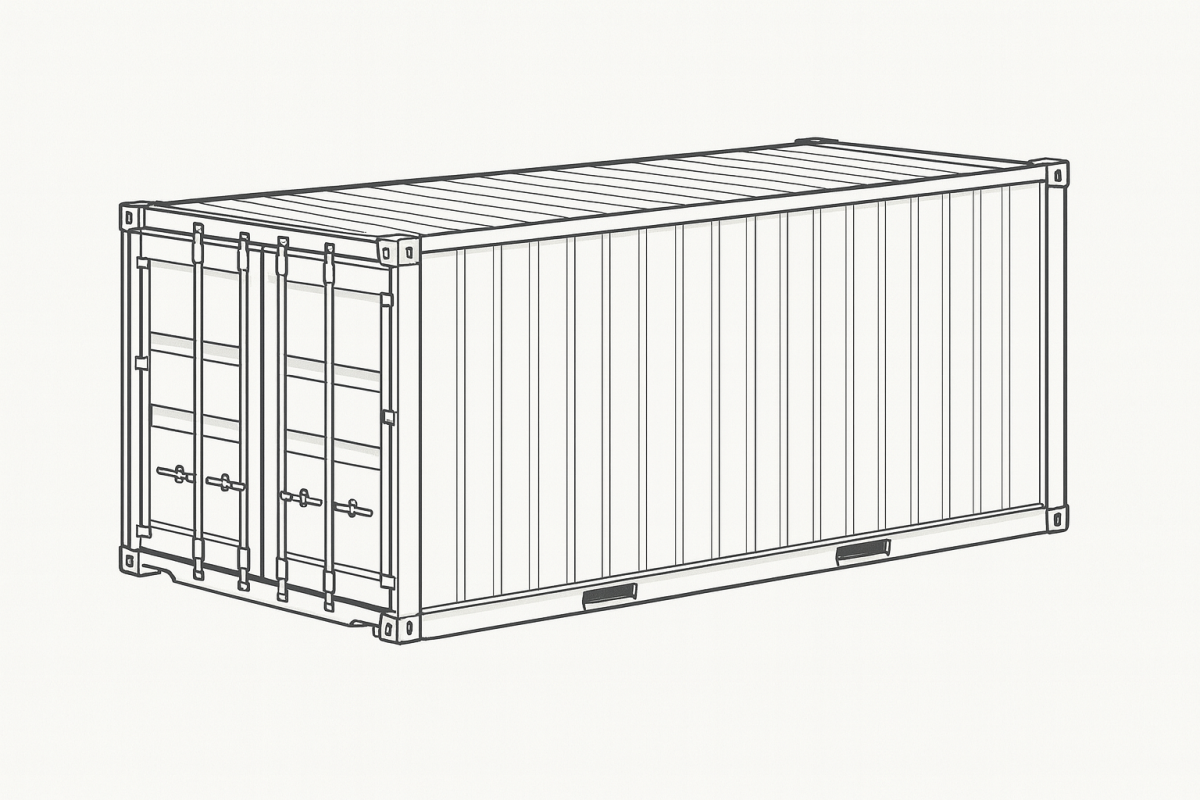
Types of Shipping Containers & Their Uses: The Fullcargo Guide
24/10/2025 Commercio Extra UE
From Milan to the World
Since 1988, Fullcargo has been connecting Italian exporters with global markets — shipping from Milan to India, South Korea, the UAE, and beyond.
Over nearly four decades, we’ve learned that choosing the right container is one of the most strategic decisions in international logistics.
This guide explains every main container type, why it exists, and when to use it — whether you’re exporting machinery, pharmaceuticals, or luxury goods.
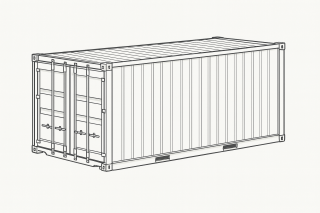
1. Dry Container (General Purpose Container)
What it is: The most common container type — fully enclosed, weatherproof, with solid walls and roof.
Why it’s used: Ideal for dry goods that don’t require temperature control.
Examples: Electronics, textiles, packaged goods, furniture.
Sizes available: 20ft and 40ft standard.
Pro tip: Perfect when your cargo is stackable and not sensitive to humidity or temperature fluctuations.
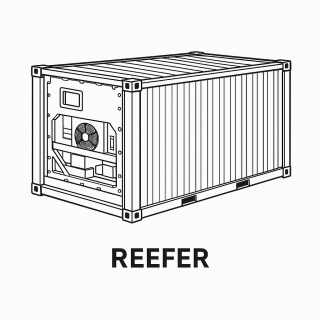
2. Reefer Container (Refrigerated Container)
What it is: A temperature-controlled container with an integrated refrigeration unit.
Why it’s used: To transport perishable items safely across long distances.
Examples: Food, dairy, pharmaceuticals, flowers.
How it works: Maintains temperatures between -30°C and +30°C, connected to vessel or terminal power.
Pro tip: Always check the temperature-monitoring system and ensure pre-cooling before loading.

3. Open Top Container
What it is: A container without a fixed roof (covered with tarpaulin).
Why it’s used: For cargo taller than the container’s height that needs loading from above.
Examples: Heavy machinery, marble blocks, construction materials.
Pro tip: Use this container for oversized freight that can’t pass through standard doors.

4. Flat Rack Container
What it is: A container with no side walls and sometimes no end walls.
Why it’s used: For heavy, wide, or irregularly shaped cargo.
Examples: Vehicles, pipes, industrial components.
Pro tip: Ideal for “project cargo” — items requiring crane loading or lashing to the deck.
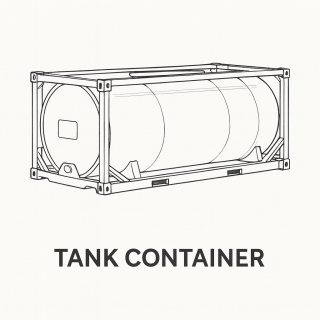
5. Tank Container
What it is: A cylindrical tank mounted inside a steel frame.
Why it’s used: To transport bulk liquids, chemicals, or gases safely.
Examples: Wine, fuel, oils, industrial chemicals.
Safety note: Each tank container follows ISO standards and requires periodic inspection.
Why Container Choice Matters in Global Logistics
Choosing the right container reduces risk, prevents delays, and optimizes shipping costs.
A container is not just a metal box — it’s a controlled environment for your product’s journey.
At Fullcargo, we help our clients:
- Identify the most efficient and secure container type.
- Optimize routes for India, South Korea, and the UAE.
- Manage documentation and customs with precision.
- Track and monitor cargo using digital freight tools.
Fullcargo: Italian Roots, Global Reach
Founded in Milan in 1988, Fullcargo has grown from a local forwarding company into a global logistics partner for industries ranging from fashion to machinery.
We ship worldwide — handling full-container loads (FCL), less-than-container loads (LCL), air freight, and project logistics.
Want to learn more?
Contact our logistics experts for a personalized consultation.